Surgical Time
6-12 hours
Anesthesia
General
Recovery
12-24 months
Hospital Stay
14-30 days
Total Stay
6-8 weeks
Back to Work
6-12 months
Intestine Transplant in Iran:
A Specialized Procedure
Intestine transplantation in Iran is a highly specialized surgical procedure that offers a life-saving option for patients with intestinal failure. This complex condition prevents the small intestine from properly absorbing nutrients, leading to severe malnutrition and dependence on intravenous feeding (total parenteral nutrition or TPN). This comprehensive article provides an overview of intestine transplantation in Iran, covering the conditions it treats, the evaluation process, the surgical procedure, and the post-transplant care involved. We will explore the challenges of intestinal failure and how intestine transplantation can offer a chance for a better quality of life.
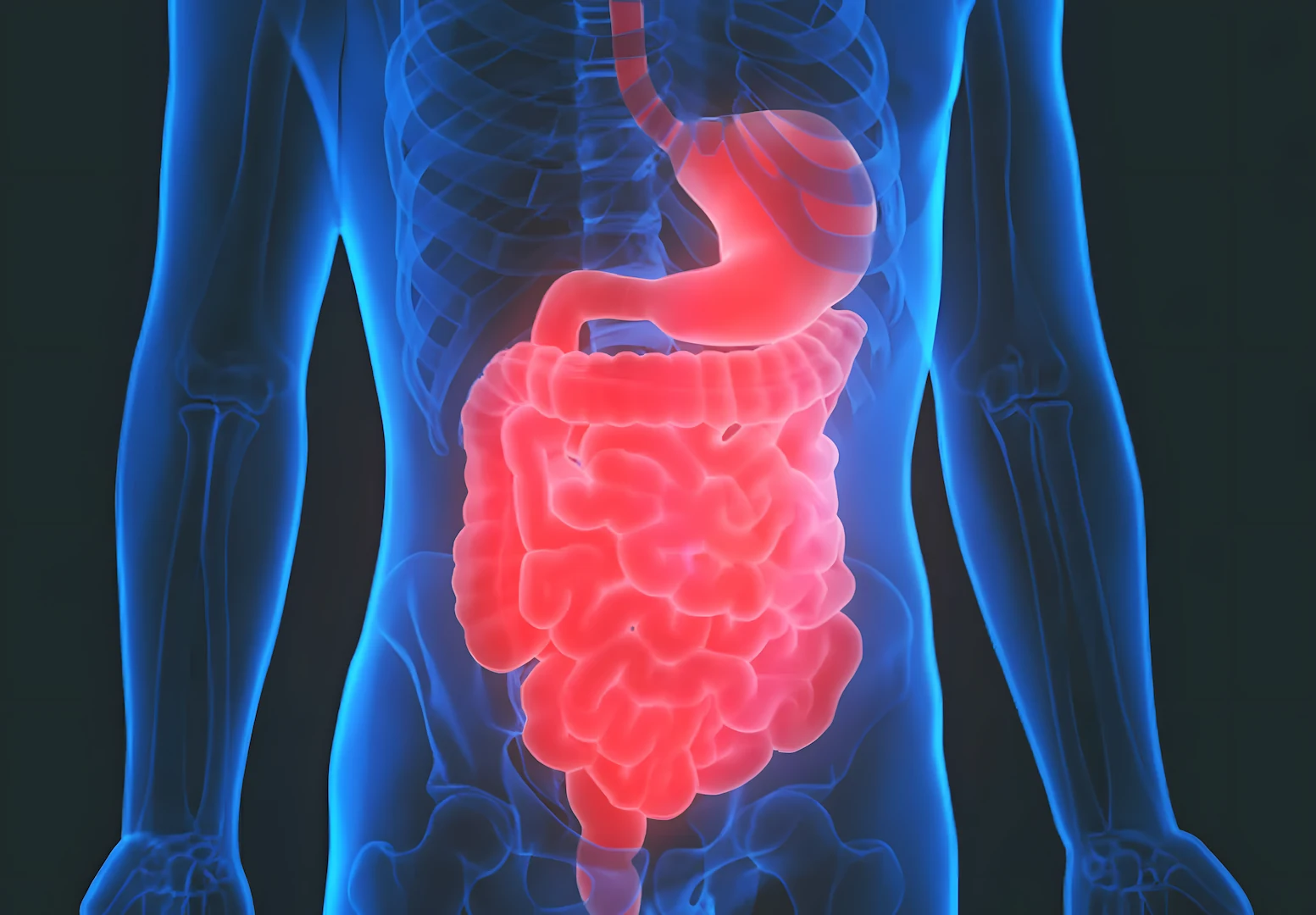
Understanding Intestine Transplantation
Intestine transplantation involves surgically replacing a diseased or severely damaged small intestine with a healthy small intestine from a donor. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing most of the nutrients from food, and when it fails, the body cannot receive the necessary nourishment. This procedure is complex and requires a highly skilled medical team.
Conditions Treated with Intestine Transplantation
Intestine transplantation in Iran is considered for patients with severe intestinal failure caused by various conditions. Some of the primary reasons for this procedure include:
Conditions Leading to Short Bowel Syndrome
Short bowel syndrome is a major indication for intestine transplantation:
- – Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS): This condition occurs when a significant portion of the small intestine is missing or does not function correctly. Causes include:
- — Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A serious intestinal disease in infants.
- — Mesenteric Infarction: Loss of blood flow to the intestine.
- — Crohn’s Disease: Severe inflammation of the digestive tract.
- — Surgical Resection: Removal of a large portion of the intestine.
Other Causes of Intestinal Failure
Less common but still significant reasons for transplant include:
- – Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction: A condition where the intestine cannot contract properly to move food through.
- – Intestinal Tumors: Rare tumors that damage intestinal function.
- – Congenital Diseases: Birth defects affecting the intestine.
Pre-Transplant Evaluation and Patient Selection in Iran
A thorough evaluation is essential to determine if a patient is a suitable candidate for intestine transplantation in Iran. This involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition:
Medical Assessments
These evaluations assess the severity of intestinal failure and the patient’s overall health:
- – Medical History and Physical Examination: Detailed review of the patient’s medical background, symptoms, and current condition.
- – Nutritional Assessment: Evaluation of the patient’s nutritional status and dependence on TPN.
- – Intestinal Function Tests: Tests to assess the remaining function of the intestine.
- – Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, or other imaging to examine the intestine and surrounding organs.
Additional Evaluations
These assessments evaluate the patient’s suitability for surgery and post-transplant care:
- – Infection Screening: Tests to rule out infections.
- – Cardiac and Pulmonary Evaluation: Assessment of heart and lung function.
- – Psychological Evaluation: Evaluation of the patient’s emotional and mental readiness for the transplant.
- – Social Evaluation: Assessment of the patient’s support system and ability to adhere to post-transplant care.
The transplant team carefully reviews all the information to determine if intestine transplantation is the best course of action.
Types of Intestine Transplantation in Iran
Intestine transplantation in Iran can involve transplanting different parts of the digestive system:
Isolated Intestine Transplantation
This involves transplanting only the small intestine.
Combined Organ Transplantation
In some cases, the intestine is transplanted along with other organs:
- – Liver-Intestine Transplantation: When both the liver and intestine are failing.
- – Multivisceral Transplantation: Transplanting the intestine along with other abdominal organs like the stomach, pancreas, and liver.
The Intestine Transplant Surgery Procedure in Iran
Intestine transplant surgery is a complex and lengthy procedure. The surgical steps generally include:
Surgical Steps
The procedure typically involves:
- – Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- – Incision: A large incision is made in the abdomen.
- – Removal of the Diseased Intestine: The damaged intestine is carefully removed.
- – Implantation of the Donor Intestine: The donor intestine is connected to the remaining digestive tract.
- – Revascularization: Connecting the blood vessels of the donor intestine to the recipient’s.
- – Closure: The abdomen is closed.
The surgical team takes great care to ensure proper blood flow and connections to the new intestine.
Post-Transplant Care and Recovery in Iran
Post-transplant care is crucial for the success of intestine transplantation. It involves:
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
This includes:
- – Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Stay: Close monitoring in the ICU.
- – Immunosuppressant Medications: Powerful medications to prevent organ rejection.
- – Infection Prevention: Measures to prevent and treat infections.
- – Monitoring Intestinal Function: Closely observing the new intestine for signs of function and complications.
Long-Term Recovery and Follow-up
This phase involves:
- – Immunosuppression Management: Lifelong management of immunosuppressant medications.
- – Nutritional Support: Gradual weaning off TPN and introducing oral feeding.
- – Monitoring for Rejection: Regular tests to detect and treat organ rejection.
- – Managing Complications: Addressing potential complications, such as infections or rejection episodes.
Outcomes and Survival Rates of Intestine Transplantation
Intestine transplantation outcomes have improved over the years, but it remains a high-risk procedure. Survival rates vary depending on the patient’s condition and other factors. Long-term survival requires careful management and ongoing medical care.
Intestine Transplantation in Iran: What to Expect
Specialized transplant centers in Iran offer intestine transplantation. These centers have multidisciplinary teams with expertise in this complex procedure. Access to intestine transplantation in Iran provides a valuable option for patients with severe intestinal failure.
Cost Considerations for Intestine Transplant in Iran
Intestine transplantation is a costly procedure due to its complexity and the need for specialized care. Costs can vary depending on the hospital and the length of the hospital stay. Compared to some Western countries, the cost of intestine transplantation in Iran may be relatively lower.
Choosing an Intestine Transplant Center in Iran
Selecting an experienced and specialized transplant center is crucial for successful intestine transplantation. Key factors to consider include:
Key Factors to Consider
- – Experienced Multidisciplinary Team: Surgeons, gastroenterologists, transplant physicians, nurses, and other specialists with expertise in intestine transplantation.
- – Advanced Facilities: A hospital with a dedicated transplant unit and intensive care facilities.
- – Comprehensive Care: A program that provides thorough pre- and post-transplant care, including nutritional support and rejection management.
- – Outcomes and Experience: The center’s track record of successful intestine transplants.
Conclusion
Intestine transplantation in Iran offers a complex but potentially life-saving treatment for patients with severe intestinal failure. Specialized centers with experienced medical teams provide this option, offering hope for improved quality of life. Understanding the procedure, the challenges involved, and the commitment to long-term care is essential for patients and their families considering intestine transplantation.